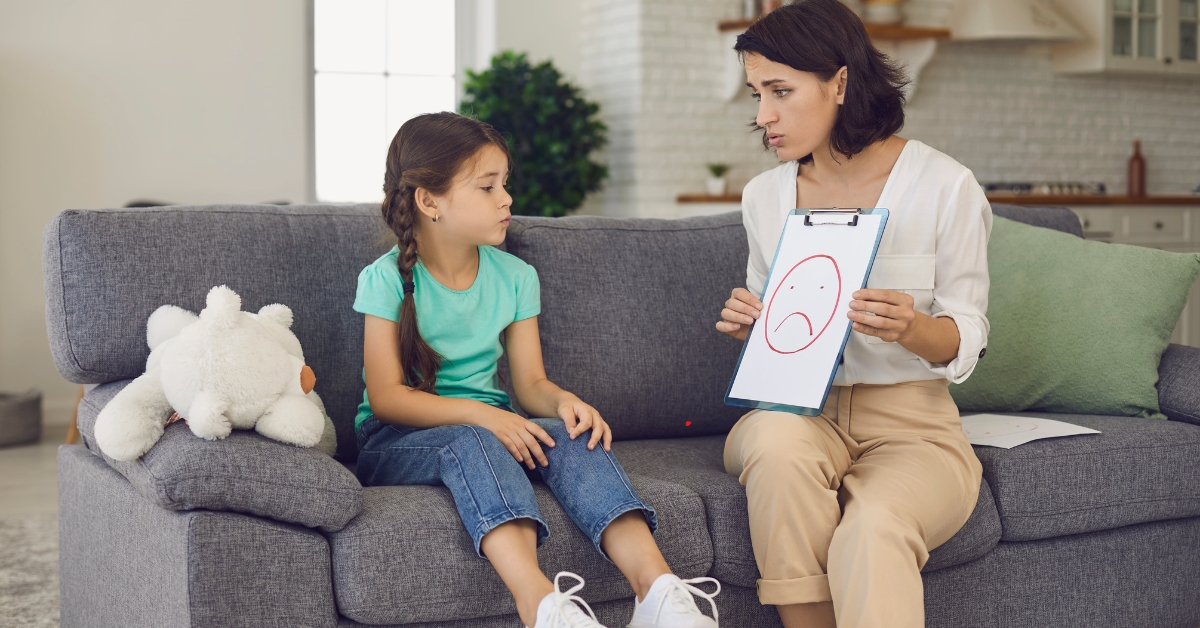
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects both children and adults. It manifests as difficulties in focusing, impulsivity, and hyperactivity, often interfering with daily life. Effective management requires a combination of strategies tailored to individual needs. This article explores ADHD treatment options, from medications to behavioral therapy, helping you choose the right approach.
What Is ADHD?
ADHD is characterized by a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity. Symptoms can vary:
- Inattention: Difficulty sustaining focus, being easily distracted.
- Hyperactivity: Excessive movement or fidgeting, even in inappropriate situations.
- Impulsivity: Acting without considering consequences.
Fact:
ADHD affects approximately 5–10% of children and 2–5% of adults worldwide, with varying severity levels.
ADHD Treatment Options
1. Medications for ADHD
Medications are often the first line of treatment for managing ADHD symptoms. They fall into two main categories:
a. Stimulants
- Examples: Methylphenidate (Ritalin), Amphetamines (Adderall).
- How They Work: Increase dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, improving focus and reducing hyperactivity.
- Effectiveness: Studies show stimulants help 70–80% of individuals with ADHD.
b. Non-Stimulants
- Examples: Atomoxetine (Strattera), Guanfacine (Intuniv).
- How They Work: Target norepinephrine pathways to improve attention and impulse control.
- Best For: Individuals who don’t respond well to stimulants or have specific health conditions.
Pharmacist Advice:
Always follow the prescribed dosage and discuss potential side effects, such as sleep disturbances or appetite changes, with your doctor.
2. Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy focuses on modifying negative behaviors and building positive habits.
For Children:
- Parent training programs help caregivers understand ADHD and implement effective strategies at home.
- Classroom interventions assist teachers in managing behaviors and improving learning outcomes.
For Adults:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) addresses time management, organization, and emotional regulation issues.
Why It Works:
Therapy equips individuals with tools to cope with challenges, complementing medication for comprehensive treatment.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Simple lifestyle changes can significantly impact ADHD management:
- Regular Exercise: Improves mood and enhances concentration by increasing dopamine levels.
- Balanced Diet: Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and protein support brain function.
- Sleep Hygiene: Consistent sleep routines reduce hyperactivity and improve focus.
Quick Tip:
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, have been shown to improve attention spans over time.
4. Educational Support
For children with ADHD, Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) or 504 Plans provide tailored learning strategies, ensuring equal opportunities in school.
Examples of Support:
- Extra time on tests.
- Breaks during long tasks.
- One-on-one assistance for complex assignments.
Pro Tip:
Advocate for your child’s needs by collaborating with educators and school counselors.
Combination Therapy: The Best of Both Worlds
Research suggests that a combination of medication and behavioral therapy yields the most effective results for ADHD management. Medications address immediate symptoms, while therapy builds long-term coping skills.
Choosing the Right Treatment
Factors to Consider:
- Severity of Symptoms: Mild cases may benefit from therapy alone, while moderate to severe cases often require medication.
- Age of the Individual: Treatment approaches differ for children and adults.
- Co-existing Conditions: Anxiety, depression, or learning disabilities may influence treatment plans.
Consultation Is Key
Speak with a healthcare provider or specialist to evaluate symptoms and create a personalized treatment plan.
Common Challenges in ADHD Treatment
Medication Side Effects
Some individuals may experience side effects like reduced appetite, insomnia, or mood swings. Adjusting dosage or switching medications can often resolve these issues.
Stigma and Misconceptions
ADHD is sometimes misunderstood, leading to stigma. Education and open communication can help dispel myths and create a supportive environment.
When to Seek Help
If symptoms of ADHD are significantly affecting your or your child’s daily life, it’s time to consult a professional. Early intervention improves outcomes and helps prevent secondary issues like low self-esteem or academic struggles.
Conclusion
Managing ADHD requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments, behavioral interventions, and lifestyle adjustments. Whether you choose medication, therapy, or a mix of both, the key is finding what works best for you or your child. With proper care and support, individuals with ADHD can thrive and lead fulfilling lives.
Take the first step today by consulting a healthcare provider to explore the best ADHD treatment options for your unique needs.